Keep your network under control with basic tools in linux.
Keep Your Network Under Control with Darkstat and Two Simple Commands
Managing and monitoring network activity is essential for maintaining control over your system's traffic. With the darkstat package, combined with just a couple of commands, you can easily keep track of what's happening on your network. Additionally, you can clean your browser at startup to prevent unwanted connections. Below is a step-by-step guide to setting this up.
1. Install Darkstat and Necessary Tools
First, you need to install darkstat and a couple of other useful packages to monitor network traffic:
sudo apt install darkstat net-tools iftop
- darkstat: A network statistics tool that captures traffic, calculates usage, and serves reports via a web interface.
- net-tools: Provides the essential network interface utilities.
- iftop: A real-time console-based bandwidth monitoring tool.
2. Use Two Simple Commands to Monitor Network Traffic
Once installed, you can monitor your network using these simple commands:
- Command 1: Monitor open network connections with
lsof:
watch -n 2 lsof -i -P -n
This command runs every 2 seconds, displaying a list of active network connections in real-time.
- Command 2: Monitor bandwidth usage with
iftop:
iftop
This provides a visual display of network bandwidth usage, showing the IP addresses and transfer rates.
3. Configure Darkstat
Darkstat requires some configuration to suit your network. Open the Darkstat configuration file at /etc/darkstat/init.cfg and adjust the following settings:
# /etc/darkstat/init.cfg
INTERFACE="-i enp4s0"
DIR="/var/lib/darkstat"
PORT="-p 666"
BINDIP="-b 0.0.0.0"
DAYLOG="--daylog darkstat.log"
- INTERFACE: Replace
enp4s0with the name of your network interface (check it usingip addr). - PORT: Sets the port on which Darkstat serves its web interface (in this case, port 666).
- BINDIP: Bind to IP address 0.0.0.0 to allow access from any address.
- DAYLOG: Specify a log file for daily statistics.
Once configured, start Darkstat using:
sudo service darkstat start
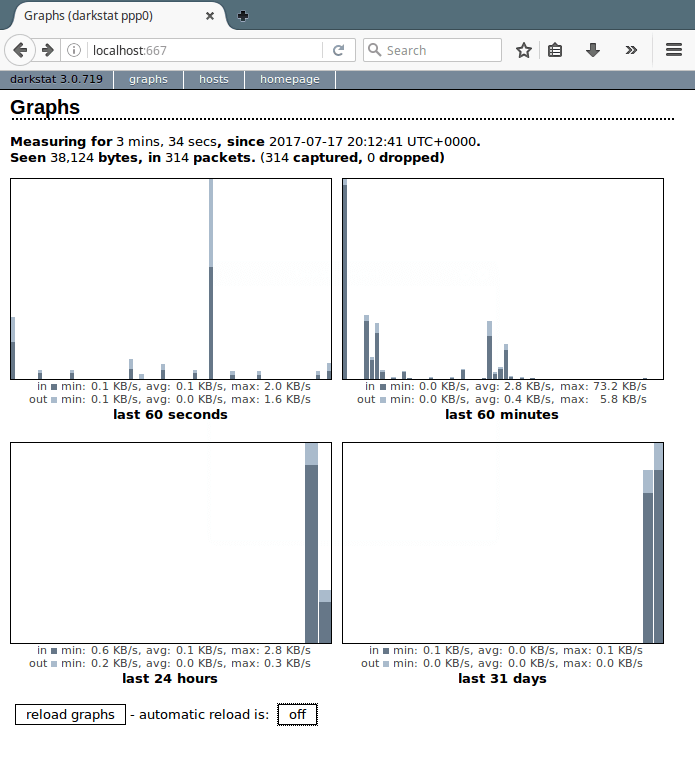
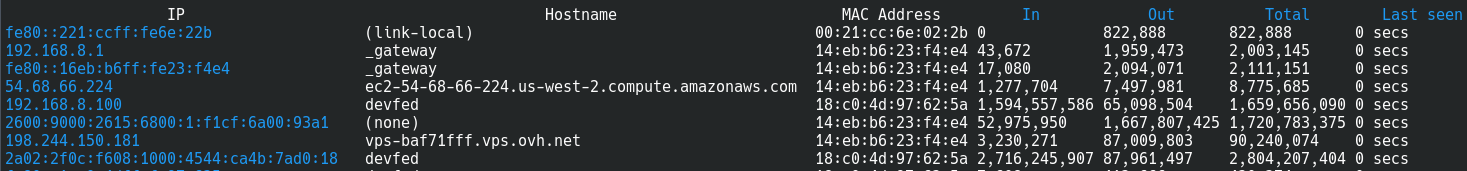
You can now access network statistics by navigating to http://localhost:666 in your browser.
4. Clean Your Browser at Startup
To prevent Firefox from making automatic connections and improve privacy, follow this guide from Mozilla Support. It provides steps to stop Firefox from initiating background connections, which can be especially useful when you want full control over your network traffic.
Conclusion
By using darkstat and simple monitoring commands like lsof and iftop, you can easily keep track of your network activity in real-time. Combined with cleaning your browser at startup, this setup ensures you maintain full control over your system’s connections and traffic.
```